Another month, another employment surprise. Should we be surprised anymore?
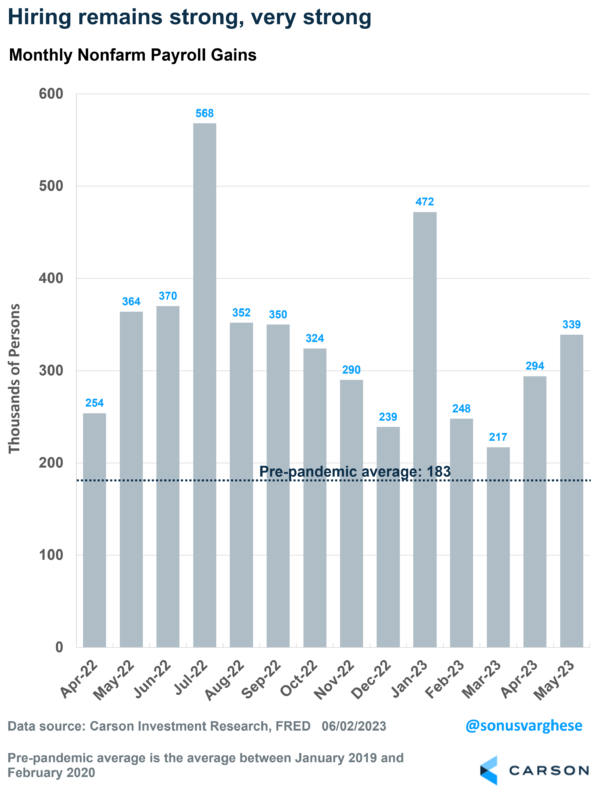
Economists expected payrolls to grow by about 187,000 in May. That’s still a solid job growth number, but a stepdown from what we’ve seen this year through April. However, actual payroll growth beat expectations for the 14th straight month.
The economy created 339,000 jobs in May, close to double expectations. Better still, payroll growth in March and April were revised higher by a total of 93,000!
- March payrolls were revised up by 52,000, from 165,000 to 217,000
- April payroll were revised up by 41,000, from 253,000 to 294,000
We’ve got two months of payroll data since the Silicon Valley Bank crisis in March, and nothing suggests weakness arising from that banking crisis.
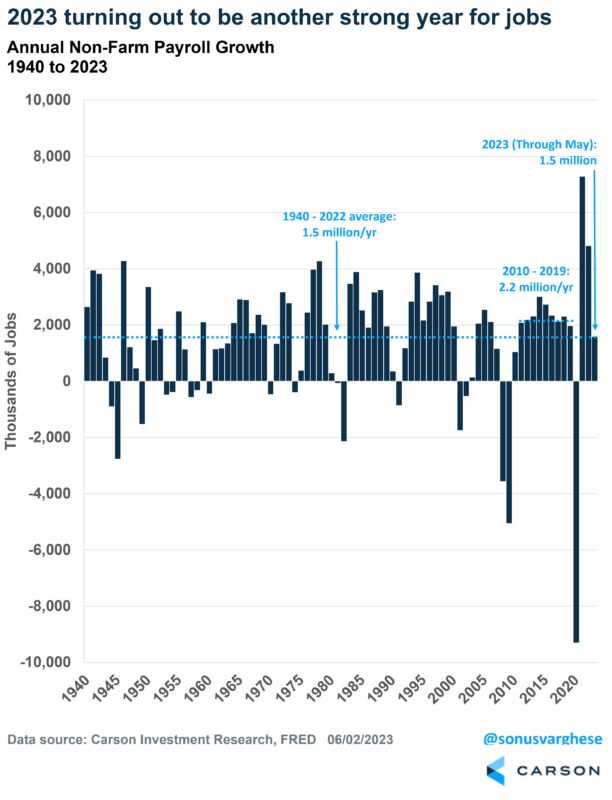
Over the first five months of the year, the economy’s added 1.5 million jobs. That in a nutshell tells you how the economy is doing. For perspective, the average annual payroll growth between 1940 and 2022 was 1.5 million. During the last expansion, 2010-2019, average annual payroll growth was 2.2 million per year.
But what about the unemployment rate?
The unemployment rate did rise from a 50-year low of 3.4% to 3.7%. This does raise some cause for concern but digging through the data suggests it may be noise more than anything else.
It probably helps to understand that the job growth and unemployment rate data come from different sources. The former comes from asking about 120,000+ businesses how many people they hired. The latter comes from asking about 60,000 households about their employment status. No surprise, the latter is noisier.
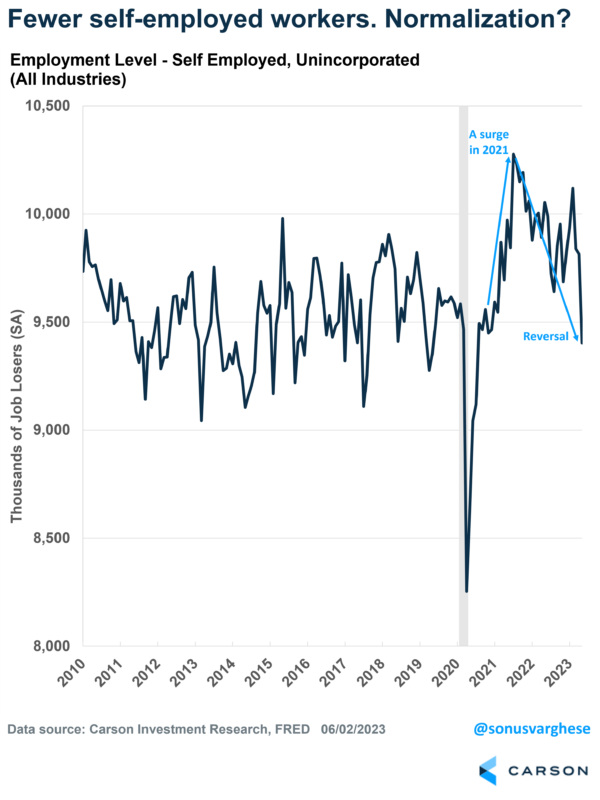
A big reason for the weak household survey (and rising unemployment rate) is that more than 400,000 people who were self-employed said they were no longer employed. As you can see in the following chart this is very noisy data, but the recent trend seems to be toward lower self-employment. It’s basically reversing the surge we saw in 2021, when self-employment surged. So, what we’re seeing now may simply be normalization of the labor market as more workers move from self-employment to W2 jobs with an employer.
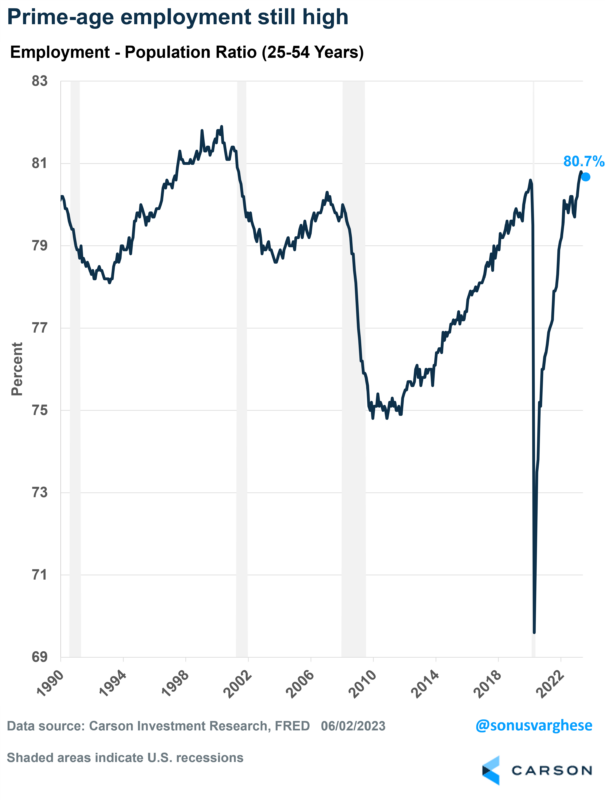
Also, the unemployment rate can be impacted by people leaving the labor force (technically defined as those “not looking for work”) and an aging population. I’ve discussed in prior blogs how we can get around this by looking at the employment-population ratio for prime age workers, i.e. workers aged 25-54 years. This measures the number of people working as a percent of the civilian population. Think of it as the opposite of the unemployment rate, and because we use prime age, you also get around the demographic issue.
The good news is that the prime-age employment-population ratio dropped only a tick, from 80.8% to 80.7%. This still leaves it higher than at any point between 2002 and 2022.
All in all, the labor market remains strong and resilient, despite all the recession calls. Perhaps its not as strong as the headline payroll growth number of 339,000 suggests, but any number above 150,000 would be good at this point. And we’re certainly well above that.

Stay on Top of Market Trends
The Carson Investment Research newsletter offers up-to-date market news, analysis and insights. Subscribe today!
"*" indicates required fields
In fact, looking at the job growth and employment-population data, this labor market is probably the strongest we’ve seen since the late 1990’s. Our view since the end of last year has been that the economy can avoid a recession this year, and nothing we’ve seen to date suggests we need to reverse that view. Far from it.